BLE Mesh: what is it and how does it work?
Ble mesh is becoming increasingly important in the world of indoor location. But what exactly is it? In this article, we shed light on what ble mesh is, how it works, supported and use cases.
- BLE Mesh is a wireless communication technology that supports both tracking and data acquisition scenarios (sensing)
- BLE Mesh technology is reliable and based on a lightweight and easy to install infrastructure
- BLE Mesh is used in various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare and smart building
As technology continues to advance, so does the way we communicate with our devices. We previously told you about Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), a wireless communication technology that has revolutionised the way we connect our devices and enabled some indoor location services. However, with the growing trend of the Internet of Things and the need to connect more and more devices, over larger and larger spaces, comes the need for distributed wireless communication networks that are easy to create and manage. This is where Bluetooth Low Energy Mesh (BLE Mesh) comes into play. In this article, we provide an overview of what BLE Mesh is, how it works, devices that support it, and use cases for this technology.
The Mesh Network
The peculiarity of a Mesh network is that it self-organises its nodes allowing indirect communication between any device within the network. There are many implementations of the way a mesh network is created, including the one offered by the Bluetooth standard and those of Wirepas and Casambi, which are industrial implementations. The latter exploit the physical communication provided by Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), i.e. the radio technology that allows two devices to communicate with each other, while implementing their own mesh network management for connectivity between devices.
BLE Mesh: devices involved and their roles
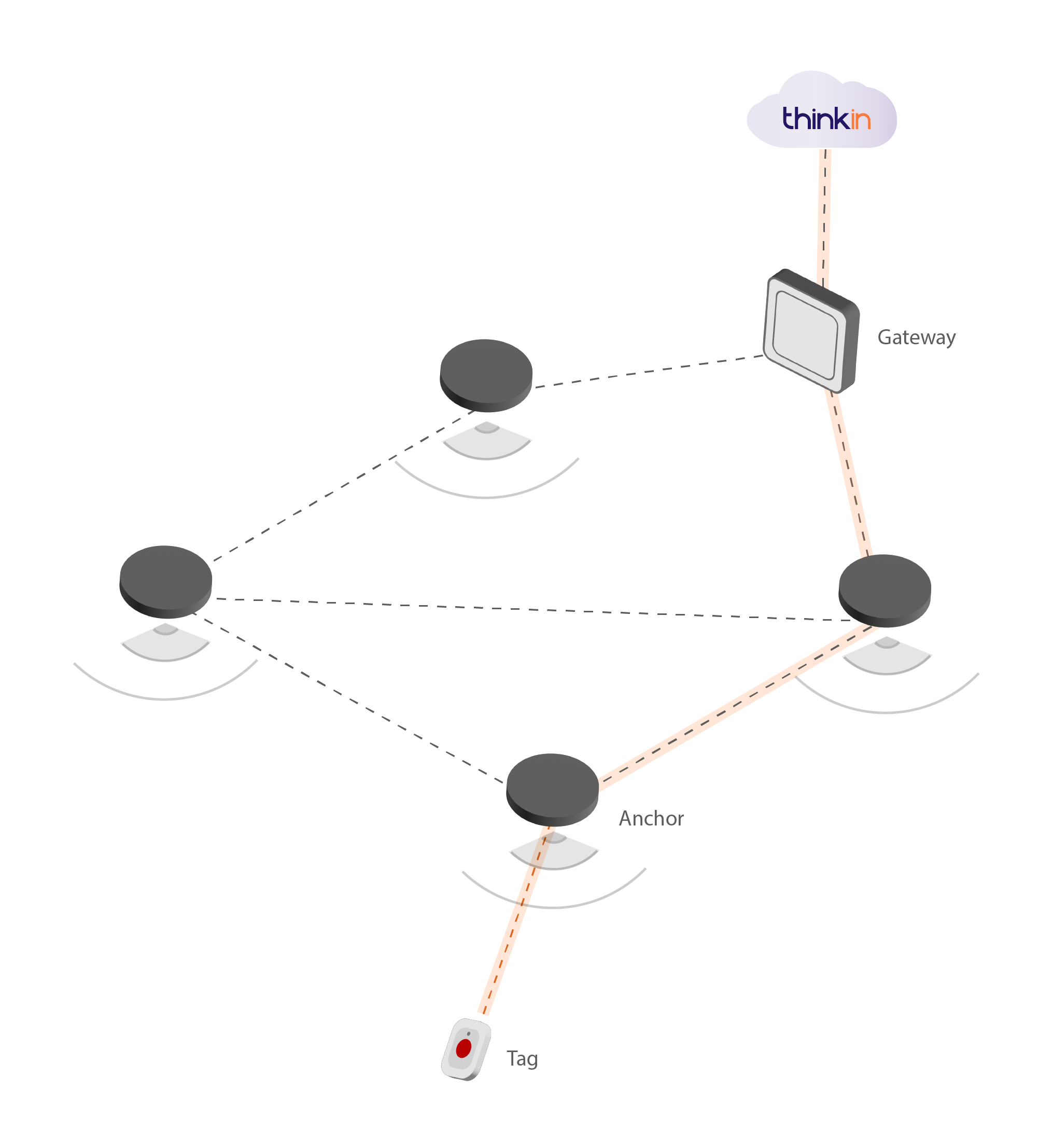
In order to operate, the BLE Mesh requires specific devices including tags, anchors and gateways. These devices, in connection with each other, allow the information collected, such as location data, to be used to provide certain services. Let us now look at the devices involved and their roles in the infrastructure.
Tags
Tags are BLE devices used for locating people, resources and objects within a space. Tags transmit a radio signal that can be detected by anchors, which enables the location of tracked resources within the space to be determined. The shape and size of tags is changeable depending on their characteristics and use, for example they can be wristbands to track patients in an RSA, or simply round or rectangular and larger or smaller to track a pallet in an industrial plant.
Anchors
Anchors are devices that are typically battery-powered and placed within a space, attached to the walls or ceilings of the facility. Anchors receive data from the tags, including location data, but not only: they can also act as sensors to detect environmental information, e.g. temperature and humidity.
Furthermore, anchors represent the nodes of the mesh network and they organise themselves autonomously within the network. Information then passes from tags to the nearest anchor and from anchor to anchor until it reaches the gateway. The greater the density of the anchors, the more precise the localisation.
Gateway
Gateways are devices that collect data from the mesh network and communicate it directly with servers in the cloud or on-premises. The gateway thus acts as a bridge between the network and the software, and only through the gateway can the information reach its destination.
Gateways also lighten the entire infrastructure, as they group the nodes of the mesh network, the anchors, to receive information more efficiently. Indeed, data transmitted through nodes alone takes longer to reach its destination. The number of gateways is also an important choice from the point of view of anchor consumption: an anchor consumes more when placed close to a gateway than an anchor located further away, as information is transmitted via the most optimised path, passing first to the anchors closest to the tags and then to those closest to the gateways.
Gateways, therefore, represent a data collection point that is then communicated directly to the software, which processes the data and uses it to deliver services or applications. For example, indoor location services such as asset tracking, process monitoring, access control, tooling and warehouse management. These types of services are applicable in various sectors, such as manufacturing, healthcare and smart building.
What are the benefits of BLE Mesh?
The advantages of using BLE Mesh over other technologies are:
- Reliability: the BLE Mesh is supported by a very robust signal even in complex working environments, ensuring proper data transmission.
- Battery life: the battery life lasts for years, BLE Mesh allows operation at a low power level, reducing power consumption.
- Scalability: the system is able to support an increasing workload, being able to accommodate thousands of nodes. The mesh structure of the network allows it to expand and self-organise by adding new nodes and deciding connections without having to redesign the entire infrastructure.
- Cost-effective: BLE Mesh has low infrastructure costs as it supports a wireless infrastructure. Generally, cabling is only required for the installation of gateways, which can be one or more depending on the needs and characteristics of the infrastructure itself.
- Infrastructure: the lightness of the infrastructure enables lean and efficient communication at the cost of lower accuracy and higher signal latency (2-5 metres, 2-3 minutes respectively).
Use cases
This type of technology is used in numerous environments, including:
- Healthcare facilities: BLE Mesh can be used in the tracking of medical equipment to reduce search times and optimise resources, as well as in the detection of environmental conditions in operating rooms and theatres. In addition, it can help healthcare organisations gain control over procedures and processes in order to reduce errors and optimise activities.
- Industrial facilities: BLE Mesh is used for asset tracking, monitoring processes, managing inventory and logistics, managing work tools, improving safety and monitoring environmental factors.
- Smart building: in the HO.RE.CA. sector for creating smart rooms and optimising processes; in the offices of companies, schools and universities for managing and optimising rooms and spaces.
In conclusion, BLE Mesh technology is present in numerous sectors and is used in different contexts and for different purposes. Due to its low infrastructure cost, scalability and reliability, BLE Mesh offers numerous advantages over other technologies. Use cases range from healthcare facilities to industrial plants and smart buildings, offering opportunities to improve operational efficiency, safety and process optimisation in various sectors. Contact us to find out how our solution can help your business.